Painful urination, burning sensation in the urethra, erectile problems and frequent toileting are all symptoms of the inflammatory process of the prostate. What is prostatitis? The disease is multifactorial, and the cause is a combination of predisposing factors that lead to inflammation. In medical practice, pathology is classified according to the course and pathogenesis of the disease. Let us consider the cause of this disease, what symptoms it will show and how to treat it.
What is prostatitis?
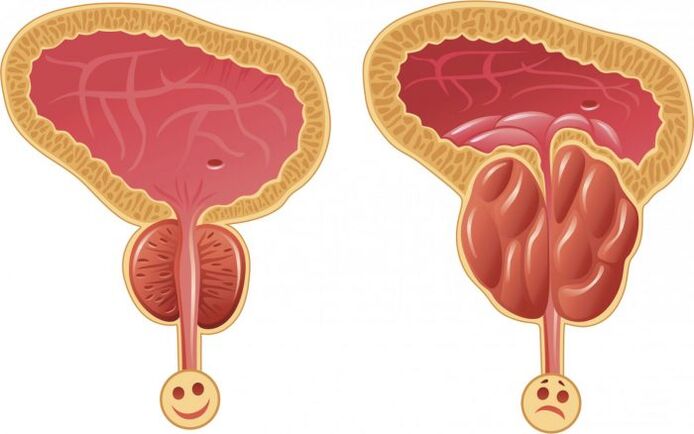
To understand what male prostatitis is, you need to know what glands are. The prostate is a male internal organ. In appearance, it resembles a "heart" or "chestnut". Ancient doctors called this organ "the second male heart".
The functions of glandular organs are as follows:
- Secret production, which is a liquid with a specific smell;
- Protect the prostate from infection;
- Maintain complete erectile function;
- Synthesis of the hormone testosterone;
- Ensure the normal process of urination.
Constantly observe the production of secretions in the prostate. In the more sexually healthy representatives, it enters the urethra during sperm secretion. Prostate secretions increase semen volume and help maintain sperm vitality.
For your reference, prostatitis is a common disease diagnosed by 80% of men, and 30% of them are diagnosed at the age of 20-40. According to static research, every tenth of people will observe pathology.
If the ultrasound shows swelling of the prostate with inflammatory lesions in it, then this is prostatitis. In most clinical pictures, the inflammatory process proceeds with the formation of stones. The male organs are surrounded by the urethra and seminiferous ducts, and the ureter is compressed due to edema. As a result, the main symptoms of the disease were revealed-urination problems-pain, cramps, burning.
When an inflammatory process occurs, the qualitative and quantitative components of the prostatic fluid will change. As a result, libido decreases, erections deteriorate, and effectiveness decreases.
Causes and symptoms of prostatitis

When it comes to prostatitis, it is impossible to tell the exact cause of the inflammatory process. Many doctors agree that the cause is based on a combination of factors.
The appearance of prostatitis is due to the following reasons:
- Infectious diseases spread during sexual intercourse.
- Violation of the blood circulation of the pelvic organs. This leads to an inactive lifestyle, tight underwear and jeans.
- Damage to the perineal organs, leading to poor blood circulation.
- Frequent hypothermia, the presence of chronic diseases of the reproductive system.
- Hormonal imbalance, irregular sex life, long-term abstinence.
- Rectal inflammation can cause prostatitis.
- Chronic constipation.
- Immune status declines. The main sources include chronic stress, unhealthy eating habits, drinking, smoking, and unbalanced diet.
- Urinary system infections, such as gonorrhea.
In fact, there are many reasons for the occurrence of pathological processes. Only when the predisposing factors are identified can we say that the prognosis is good.
Prostatitis is divided into acute and chronic. In the first case, the man’s body temperature rises significantly and he often goes to the toilet, accompanied by severe pain syndrome and weak urine pressure. Usually, such a clinic will be accompanied by a burning sensation in the perineum and a pain in the rectum during defecation.
It is worth knowing:With the opening of the purulent inflammation and abscess of the prostate, the purulent mass is discharged from the urethra or rectum.
In the chronic process of pathology, the symptoms are not very obvious. The patient was diagnosed in the following clinics:
- Low-grade fever, which does not go away for a long time;
- Pain in the pubic area;
- Bowel problems;
- Constant fatigue, unreasonable tension and irritability.
In the context of glandular organ inflammation, dysuria is a special danger. Without proper treatment, it can lead to serious consequences-acute urinary retention.
Types of prostatitis
Therefore, to understand all the information about male prostatitis, you need to consider the form of the disease. First, there is an acute and chronic inflammatory process. The name "sharp" speaks for itself. This indicates that there is an inflammatory process caused by infection. In most cases, microorganisms are the simplest microorganisms or fungi.
In the absence of treatment for the acute form of pathology, it can transform into a chronic course, which may lead to complications in the form of benign glandular hyperplasia. The symptoms are not obvious, which is the danger of this type of disease.
The cause of chronic prostatitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms and other reasons. For example, stagnation of pelvic organs, age-related changes.
important:Bacterial prostatitis is divided into acute and chronic. Inflammation is caused by bacteria-Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus, Klebsiella. In most cases, this type is diagnosed in men between 20 and 40 years old. Compared with other types of prostatitis, it occurs in 5-10% of clinical pictures.
Other types of prostate inflammation:
- The stone form of prostatitis is characterized by an inflammatory process that develops due to the formation of stones in the prostate. In most cases, it is diagnosed in elderly patients who neglect acute forms of medication. A neglected stone disease can cause impaired reproductive function, infertility, impotence, adenoma and other complications.
- The stagnant form of the disease most often progresses in a chronic form, and the cause is non-infectious. The main reason is blood stagnation in the pelvic organs, for example, impaired pelvic blood circulation or stagnant prostate secretions due to irregular intimate life.
- Due to the activity of pathogenic bacteria, infectious diseases will develop. In most pictures, the test will detect E. coli. There are acute and chronic courses, and the clinical and bacterial species are similar.
- The purulent form is the most dangerous type of pathology. In medicine, purulent prostatitis is divided into other types. Catharsis develops with the progress of sore throat and flu under the background of weak immune status. Follicular prostatitis is already the second stage of purulent disease; pus is discharged into the prostate, accompanied by severe pain syndrome and elevated body temperature. The substantial form is a serious form that requires prompt treatment. For abscesses in glandular organs, they are talking about abscess disease; treatment should be started immediately because of the threat of sepsis.
The treatment options for prostate inflammation are due to specific types of pathology, which may vary significantly. You can combine medication with physical therapy procedures and alternative therapies.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
In order to diagnose inflammation, the doctor will collect the patient's medical records, and then prescribe laboratory and instrumental research methods. They allow error-free diagnosis based on certain indicators.
fact:You can suspect prostatitis by performing a rectal examination of the prostate. Soreness in the anterior rectal area and increased organ size are characteristic signs of inflammation.
After rectal palpation, the following diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound examination shows the size of organs, symptoms of inflammatory process, and changes in soft tissue structure;
- The study of prostate secretions allows you to determine its composition and deviation from the norm;
- The study of urine and urethral mucosa smears will help determine the infectious diseases transmitted during sexual intercourse;
- Assess hormonal status. Too much hormonal substances can lead to pathological hyperplasia of glandular organs, and reduced hormonal concentration can lead to dysfunction.
In the diagnosis of medical experts, it is not the inflammation itself that is of interest, because it can be detected by palpation of the prostate, but the cause of the disease. After all, determining the correct predisposing factors can allow you to prescribe an effective treatment plan.
Disease treatment
The treatment of prostatitis is always a complicated process, including taking various drugs. With the permission of the attending doctor, the use of traditional treatments is not prohibited.
Treatment activities include:
- Antibacterial pills, immune stimulants, anti-inflammatory drugs. The dose, frequency and duration of use are determined individually. Medicines can be purchased at pharmacies, many of which require a doctor’s prescription.
- Physical therapy operations-use of magnetic fields, leech therapy, ultrasound and laser therapy.
- Massage the prostate. It allows you to strengthen the reproductive system and normalize the blood circulation of the prostate and pelvic organs.
Traditional treatment methods include decoctions and infusions based on medicinal materials. Patient comments pointed out that the rhizomes of red roots, licorice and marshmallows have high therapeutic effects.
important:To cure prostatitis, the prescribed treatment plan must be strictly followed. Self-administration of drugs, even the most effective drugs, may not achieve the desired results. There is no single treatment strategy: the method of helping one patient harms the second patient.
Precaution
Prostatitis is one of the more preventable diseases. For a long time, doctors have formulated preventive measures to rule out this disease. Prevention is primary and secondary. In the second case, it aims to prevent the recurrence of chronic diseases.
Precaution:
- physical activities;
- Regular intercourse
- Exclude promiscuity;
- Treat all accompanying pathologies promptly;
- Preventive examination by urologists;
- Proper nutrition and reject bad eating habits.
Preventing prostate inflammation does not require much time and capital investment, and the effectiveness of the measures is undeniable.
Prostatitis is a common disease. The self-healing rate is very low. Lack of adequate treatment can lead to a chronic course of the disease, which can worsen regularly and may lead to organ proliferation or tumors.































