The relevance of studying the mechanisms of chronic prostatitis development is proportional to the increase in the number of confirmed cases. It is well known that chronic prostatitis (CP) ranks first among urological diseases and is the result of many factors that are indispensable in modern life (social environment, ecology, increased resistance of pathogens to antimicrobial drugs).
Because the disease not only covers an increasing proportion of the male population, but is also diagnosed at an increasingly younger age, physicians treating with template regimens tend to be rather dismissive of the problem and unable to lead recovery.
What is chronic prostatitis
The diagnosis of chronic prostatitis (CP) combines a fairly wide range of pathological processes in the prostate, manifesting as a chronic inflammatory process of the tissue. However, CP cannot be viewed solely as a result of pathogen infiltration into the prostate, as this view justifies attempts to treat prostatitis with antibiotics alone, which almost never lead to lasting positive outcomes.
The main factor in the development of the pathology can be considered as the complex changes of the tissue, therefore, the functional capacity of the glands is the main reason for the development of the infectious microflora. To a certain extent, chronic prostatitis is a comprehensive diagnosis that combines several factors:
- decrease in immunity.
- The stasis process of the pelvic organs.
- Urodynamic disorders.
- Degenerative processes of the prostate parenchyma.
- Nutritional disturbances.
- inflammatory process.
development mechanism
The penetration of pathogenic flora into a healthy prostate does not actually cause an inflammatory process, since the prostatic flora is somewhat resistant to pathogens present in the urethra. However, the presence of one or more of the above-mentioned stimuli can lead to the development of persistent inflammation with accompanying scarring.fibrosis) or necrotic areas.
The proliferation of connective tissue during scarring leads to a process of hyperemia in the acini (ducts that ensure the excretion of secretions), which aggravates the course of the disease. The necrosis of the tissue leads to the formation of the cavernous cavity, which, in addition to dead epithelial cells, accumulates the secrets of the prostate.
Therefore, the main cause of CP is not infection, but various physiological disorders that make the inflammatory process chronic.
Another distinguishing feature of the disease, which makes diagnosis difficult, is theflow periodicity. Often, under the influence of external factors or the internal state of the body, there are periodic changes in the intensity of the pathology, during which acute conditions are replaced by periods of remission.
Not only is there usually no symptoms at all, but there are no laboratory indicators (eg, white blood cells) that indicate the presence of infection. Despite the positive results, this condition cannot be considered a recovery, as all physiological disturbances in the glands have not changed.
reason
The main causes of pelvic organ circulatory disturbance and prostatic venous blood stasis are:
- Remain seated permanently.
- Hypothermia throughout the body or directly in the pelvic area.
- Systemic constipation.
- Prolonged abstinence or excessive sexual activity.
- Chronic infection of any location in the body (sinusitis, bronchitis).
- Excessive physical activity, along with a lack of sleep or rest, can lead to immunosuppression.
- History of genitourinary infection (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis).
- Toxic effects on the body due to the systemic use of alcoholic beverages.
The presence of any of these causes leads to the appearance of a stagnant process, a deterioration of the excretory function of the glands, a decrease in the resistance of the cells to disease, which helps to create optimal conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms in the prostate.
Can chronic prostatitis be cured?
Although there is a wealth of systematic information on the mechanisms of CP development,its treatment is very difficultis one of the major problems in modern urological practice.
Since the disease progresses in each individual patient according to an individual protocol, the treatment approach should also be individual, taking into account all the physiological changes that take place in the prostate.
The anatomical features of the prostate can be accessed through the urethra or rectum, significantly reducing the effectiveness of applied therapeutic effects. In this regard, to achieve a relatively stable effect, a long course of treatment (usually several months) is required, during which the patient must strictly comply with all the requirements of the doctor.

Unfortunately, only a complete cure can be achieved30 out of 100. This is mainly due to not seeking prompt medical help, due to prolonged absence of severe symptoms or conscious avoidance of unpleasant diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Usually, during treatment, the shrinking process of the prostate is irreversible, and even after long-term treatment, symptoms can only be completely eliminated and a stable remission can be achieved. The duration depends on the patient's compliance and the doctor's advice.
treat
Comprehensive measures for treating CP include:
Antibacterial treatment
The activity of bacterial microflora can be suppressed with the help of antibiotics only after complex laboratory tests, on the basis of the results of which the most effective drugs are prescribed.
Typically, antibiotics are given for at least 30 days depending on the severity of the disease. Interruption of treatment is not acceptable because the remaining microbes will become resistant to this group of drugs, requiring subsequent replacement of them, or even longer courses of treatment. In the treatment of prostatitis, antibiotics with a bactericidal effect are preferentially used:
- Fluoroquinolones;
- Azalactone;
- aminoglycosides;
- tetracycline.
Nitroimidazoles or antivirals are prescribed at the same time as antibiotics if laboratory tests show a specific nature of the infection, such as trichomoniasis or prostatitis of viral origin.
Use of antispasmodics and alpha-blockers
The main purpose of using this series of drugs is to relieve pelvic floor spasm, help increase blood supply, improve urine flow, and relieve pain.
laxative
To avoid undue stress on the pelvic muscles during bowel movements, laxatives are recommended, as attempts during constipation can aggravate the patient's condition.
physiotherapy
One of the most common physical treatments is rectal massage of the prostate. The therapeutic effect of finger-banging the prostate through the anus is to squeeze out the secret of the infection, which is subsequently excreted through the urethra.
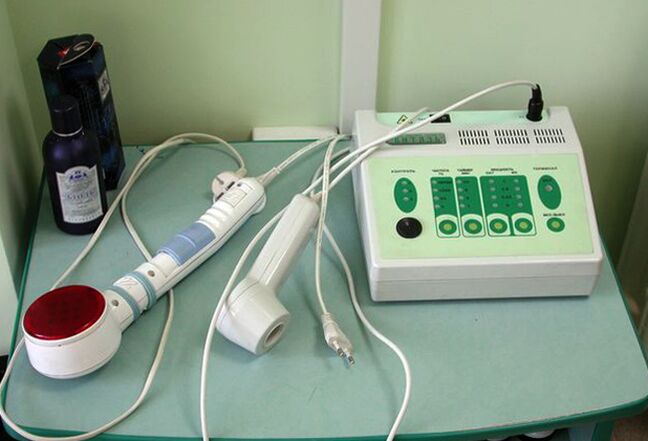
In addition, during the massage, the blood supply to the tissues increases, which has a positive effect on antibiotic therapy. For rectal prostate massage, the following physical therapy methods are also used:
- Electrical simulation.
- High frequency hyperthermia.
- Infrared laser therapy.
prevention
Once the condition is stabilized, the patient is asked to follow the rules that impose some restrictions on the usual lifestyle:
- Avoid watering procedures in open reservoirs and pools.
- Get regular doctor checkups.
- Avoid alcohol completely.
- Have regular sex with a partner.
Following the rules will keep you in remission for as long as possible and keep the disease from getting worse.































