reason
- Hypothermia and stress. The body's defenses decrease, leading to the emergence of inflammatory processes.
- Hormone imbalance. Sex hormone levels influence the activity of the prostate.
- Sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections.
- Various disorders of the body's mechanisms: urinary disorders, pelvic congestion. A low-motivation lifestyle and tight underwear can interfere with blood circulation in the pelvis. Urination problems can irritate glandular tissue and cause prostatitis. Constipation can also be considered a trigger.
- Long-term abstinence, interruption of sexual intercourse or artificially prolonged sexual intercourse. This causes the glands to enlarge and become inflamed.
- Malnutrition and alcoholism.
- Descend - Enter with the flow of urine.
- Ascending - rising along the urethra.
- Lymphogenicity - With the flow of lymph fluid.
- Hemogenous - With the flow of blood.
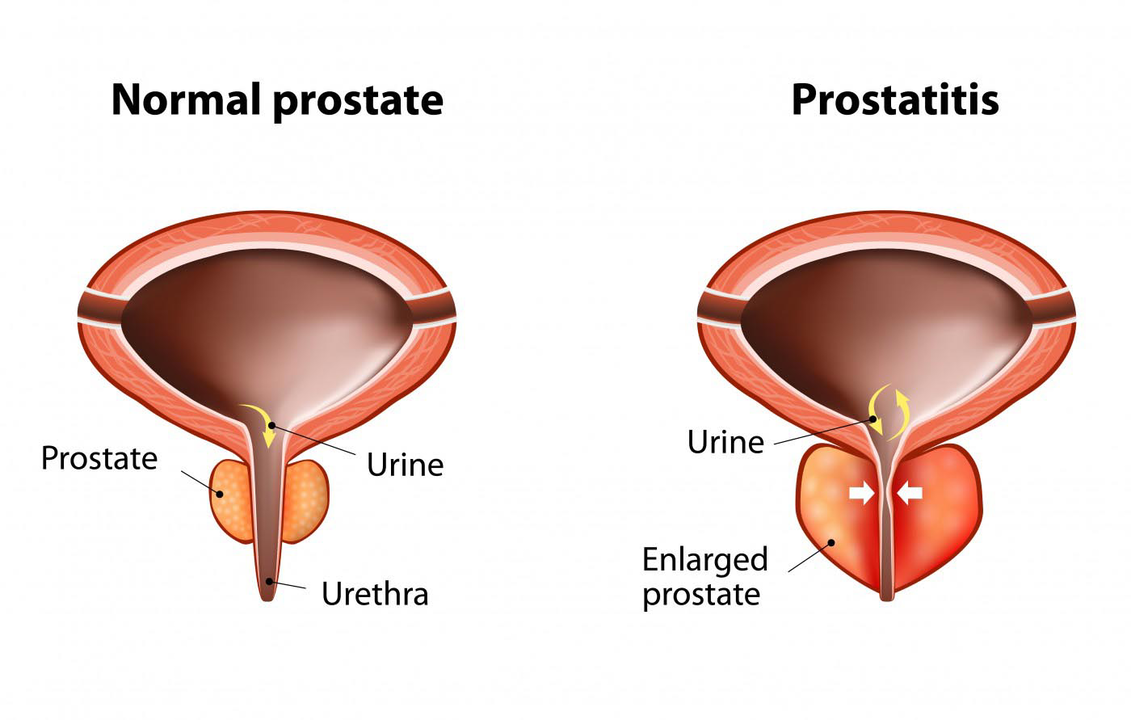
Signs and symptoms of prostatitis
- Urination problems - frequent, intermittent, and difficult;
- worsening of erection;
- burning sensation in groin;
- Urine that is cloudy and contains fiber;
- The climax is not bright;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased effectiveness;
- Depression, anxiety.
- Follicular acute prostatitis is characterized by weak water pressure during urination. It is accompanied by severe pain that can radiate to the anal area and is especially aggravated during bowel movements. Temperatures may rise slightly.
- Parenchymal acute prostatitis is characterized by unexpected perineal pain with pulsations. Observe the poisoning situation in the body, the temperature can reach 40 degrees. Often accompanied by urinary retention.
- Catarrhal acute prostatitis can cause perineal pain, frequent urination, and pain during urination.
- Decreased erection and libido;
- Water pressure decreases during urination;
- Cramping and pain during urination;
- Pain in the perineum, anus, and sacrum.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
- Prostatitis is diagnosed by rectal palpation of the prostate. It will show pain and increase in size, which are characteristic signs of the inflammatory process, and during palpation the secretions of the prostate are released and sent for analysis.
- Ultrasonography.
- Microscopic examination of prostate secretions.
- Urine bacteriological examination.
- Smears of mucosal and glandular secretions used to detect infection.
- Urethral smears are analyzed to identify sexually transmitted infections that may be causing prostatitis.
- Blood tests to determine sex hormones.
Treatment of prostatitis
- Rectal suppository. Reduce pain and relieve inflammation;
- injection;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Instillation – Injecting medication directly into the prostate;
- microenema;
- Tablet drugs. The most common are antibacterial drugs;
- Alpha-blockers.
Traditional treatments at home
- Treat prostatitis with pumpkin seeds. Pumpkin seeds contain a lot of zinc, which is necessary for men, whether they have prostatitis or not.
- Treat prostatitis with parsley - helps relieve inflammation and normalize sexual function. Contains lots of vitamins.
- Treatment of prostatitis with hemlock and celandine infusion. This method should be used with caution as these herbs are toxic and dosage and dosing regimen must be strictly adhered to.
- Use mugwort to treat prostatitis. Used to relieve inflammation and clear purulent infections.
- Use garlic, dill, hazelnuts, chestnuts, propolis, herbs, etc. to treat prostatitis.
consequences of prostatitis
- infertility;
- Impotence;
- enlarged prostate;
- Prostate cancer, etc.
Prevent prostatitis
- Sports activities. They help improve blood circulation in the pelvis, prevent congestion, and strengthen the pelvic muscles.
- Sex life rules. It is not advisable to artificially prolong sexual intercourse, interrupt sexual intercourse, or use drugs to inhibit ejaculation.
- Say no to promiscuity. Violent sex can lead to sexually transmitted infections.
- Proper, healthy nutrition.
- Quit drinking.
- Strengthen the body's defenses to avoid hypothermia.
- Minimize stress.































